Introduction
Redis Setup through Ansible using role streamlines deployment. Ansible, an automation tool, simplifies the configuration and management of Redis instances, ensuring consistency across servers. By defining tasks in Ansible playbooks, one can easily orchestrate the installation, configuration, and even scaling of Redis.
Leveraging Ansible’s idempotent nature, it ensures that repeated executions maintain the desired state, whether deploying a single instance or managing a cluster. The playbook structure facilitates customization, allowing users to specify Redis versions, ports, authentication, and other parameters. This systematic approach saves time and ensures reliability and uniformity in deploying Redis across diverse environments or multiple servers effortlessly.
Prerequisite
Major steps in redis setup through Ansible using Role
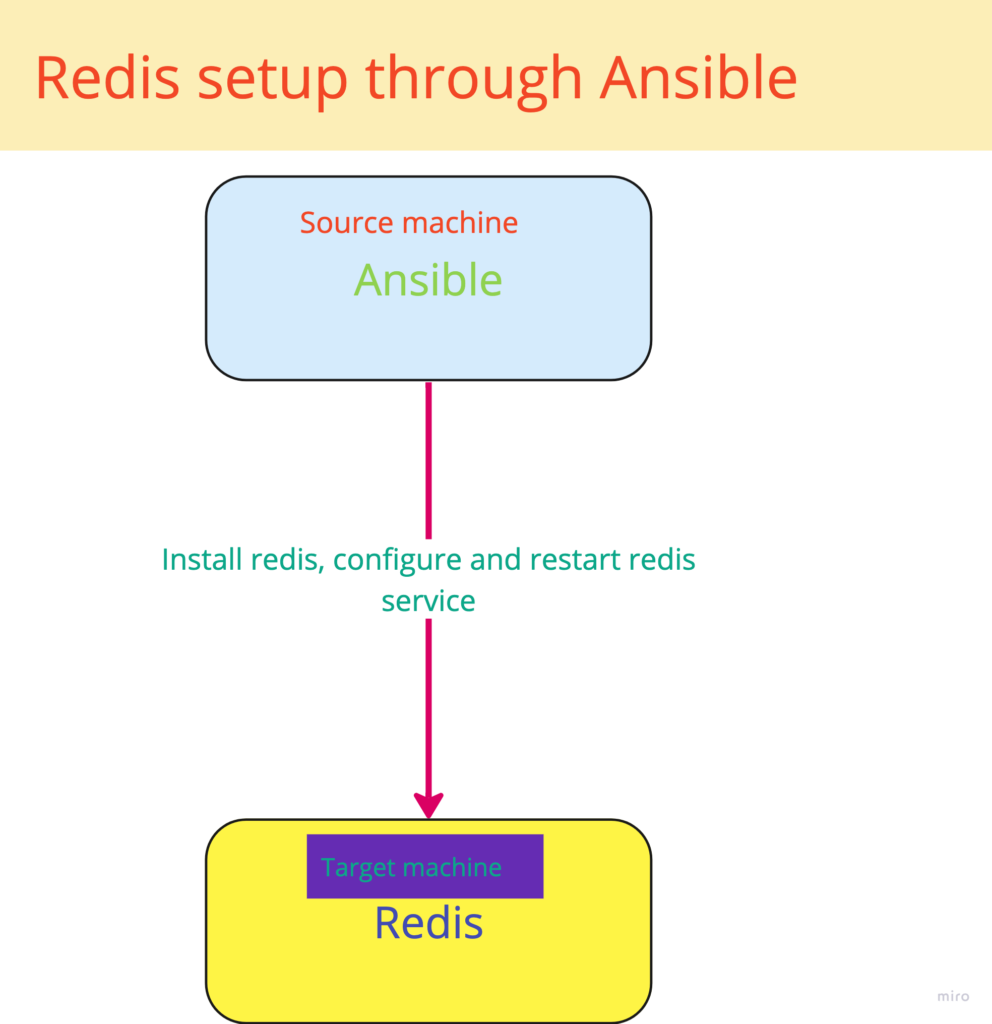
- Create redis role
- Add redis apt repository
- Install redis
- Customise redis.conf
- Restart redis server
Let us do this by using roles (learn about Role in Ansible).
Let us understand each subtask in more detail.
Create redis role
cd /path/to/ansible
# creates roles dir if if does not exists as below
mkdir roles
cd roles
# create redis role
ansible-galaxy role init redisCreate tasks for redis role
Set the default Redis version and port in defaults/main.yml
Add below content in defaults/main.yml
---
# defaults file for redis
version: 6:7.2.4-*
port: 6379
Add required tasks to setup redis in tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for redis
- name: Remove existing Redis keyring file
file:
path: /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg
state: absent
- name: Add Redis GPG Key
shell: curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | sudo gpg --batch --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg
- name: Add Redis APT Repository
shell: echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.list
- name: Install redis
apt:
name: redis={{version}}
state: present
update_cache: yes
- name: Create systemd redis service file
template:
src: redis.service.j2
dest: /etc/systemd/system/redis-server.service
mode: 0644
- name: Update /etc/redis/redis.conf
blockinfile:
path: /etc/redis/redis.conf
block: |
port {{port}}
protected-mode no
supervised systemd
notify:
- Restart redis-server service
Add redis-server handler in handlers/main.yml
---
# handlers file for redis
- name: Restart redis-server service
systemd:
name: redis-server
state: restarted
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
Inventory setup
Create inventory/prod/redis_servers.yml
Note: Please change the inventory file as per your need.
Add below contents
all:
children:
redis_servers:
hosts:
redis_server_01:
redis_server_02:
Redis playbook setup
Create the redis_servers.yml file in the playbooks folder and add the below content.
# redis_servers.yml
- name: Redis server setup
hosts: redis_servers
become: yes
roles:
- ../roles/redis
Run the playbook for redis setup
cd playbooks
# check if everything is ok using --check
ansible-playbook redis_servers.yml -i inventory/prod/redis_servers.yml -l redis_server-01 --check
# install redis-server on a single redis instance(machine)
ansible-playbook redis_servers.yml -i inventory/prod/redis_servers.yml -l redis_server-01
# install redis-server on all redis instances(machines)
ansible-playbook redis_servers.yml -i inventory/prod/redis_servers.yml
Note: We should execute the setup on a single host(instance or machine) first, then if everything is ok we can execute it on all other hosts.
Optional: Delete other created files and folders by default.
Finally, your redis role directory should look as below:

Key Takeaways
- How to set up redis using role in Ansible
- Details of tasks in redis role
- How to use a handler in a role
- How to set default values of variables
- Extend this role by adding template files inside roles/redis/templates and using them in tasks/main.yml
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1 – My playbook execution failed, how to resolve it?
Answer – First increase verbosity level in playbook execution to get more details on error. Most of the time redis errors are self-explanatory, follow and understand the error and you will be able to fix it.
E.g – Error – host unreachable
It means that ssh <host> is not working, first fix it then execute the playbook again.
Q2 – How do I validate that the redis server setup is successful?
Answer – Just log into a server, manually validate service status (sudo systemctl status redis-server), launch redis-cli, do some set, and get operations.
Conclusion
The utilization of Ansible for Redis setup culminates in a streamlined and efficient deployment process, emphasizing automation’s prowess in simplifying complex configurations. This approach, elucidated in the guide, facilitates the swift and standardized provisioning of Redis across multiple hosts.
The guide’s comprehensive instructions empower users to navigate through setting up Redis, defining configurations, and optimizing performance seamlessly. Ansible’s role in Redis setup expedites deployment and ensures uniformity and reliability across diverse environments.
Embracing Ansible for Redis provisioning showcases the power of automation in enhancing scalability, reducing manual intervention, and fostering efficient management of in-memory data stores for modern applications and infrastructures.
Enjoy the post!
4 thoughts on “Automate Redis Setup through Ansible using Role in 5 Easy Steps”